The Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) shipping agreement is a popular Incoterm used in international trade, where the seller takes on the responsibility of delivering goods to the buyer’s location while covering all costs, including shipping, insurance, and customs duties. This agreement can simplify the buying process for importers, making it an attractive option for many businesses. However, like all shipping agreements, DDP has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that both sellers and buyers must carefully evaluate.
This comprehensive guide will explore the advantages and disadvantages of the DDP shipping agreement, helping you understand when it is the right choice for your business. We’ll cover everything from the responsibilities of the seller and buyer, the cost implications, and common challenges associated with DDP.

What Is DDP Shipping?
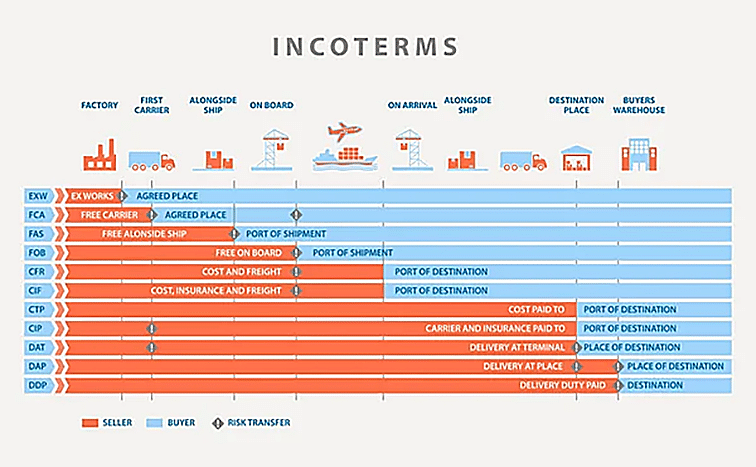
Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) is one of the 11 Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). Under DDP, the seller assumes all responsibility for delivering goods to the buyer’s location, including costs such as shipping, insurance, customs clearance, and duties. Essentially, the seller handles all aspects of the logistics process, making it easy for the buyer to receive their goods without worrying about import processes.
DDP can be used for various modes of transportation, including air, sea, and land. It provides a door-to-door delivery service, which can be highly convenient for the buyer.
Advantages of DDP Shipping Agreement
1. Convenience for the Buyer
One of the biggest advantages of the DDP shipping agreement is convenience, particularly for the buyer. Since the seller manages all aspects of the shipping process, including customs clearance, duties, and local delivery, the buyer benefits from a streamlined process. This convenience is particularly valuable for businesses that do not have expertise in handling international shipping logistics.
2. Simplified Customs Clearance
With DDP, the seller is responsible for customs clearance in the buyer’s country. This can be advantageous for buyers who may not be familiar with local customs regulations or processes. By having the seller handle customs documentation and payment of duties, buyers can avoid unexpected complications or delays at the border.
3. Predictable Costs
For the buyer, DDP shipping provides cost certainty. Since the seller includes all shipping, insurance, and customs duty costs in the total price, the buyer knows exactly how much they need to pay. This predictability can help businesses with budgeting and financial planning, as there are no hidden costs or surprises during the shipping process.
4. Reduced Risk for the Buyer
Under DDP, the seller assumes most of the risks involved in the shipping process, including the risks associated with customs clearance and payment of duties. The buyer can focus on other aspects of their business, knowing that the seller is managing all potential issues related to the delivery of goods.
5. Better Customer Experience
DDP shipping is often preferred in business-to-consumer (B2C) transactions, as it provides a seamless experience for the customer. By delivering the product directly to the buyer’s doorstep without any additional costs or paperwork, the seller enhances the overall customer experience, potentially leading to higher customer satisfaction and repeat purchases.

Disadvantages of DDP Shipping Agreement
1. Higher Costs for the Seller
One of the main disadvantages of the DDP shipping agreement is that it can be costly for the seller. The seller is responsible for covering all shipping, insurance, and customs duty costs, which can add up significantly—especially if the goods are being shipped to a country with high import taxes or if the shipment requires specialized handling. These costs may ultimately reduce the seller’s profit margin.
2. Complexity in Handling Customs
Handling customs clearance in the buyer’s country can be challenging for sellers, especially if they are unfamiliar with the local regulations. Customs processes vary from country to country, and staying compliant can be difficult and time-consuming. The seller must also navigate language barriers and manage communication with customs authorities in the buyer’s country, which can be a complex process.
3. Increased Risk for the Seller
Under the DDP agreement, the seller assumes a higher level of risk compared to other Incoterms. The seller is responsible for the goods throughout the entire shipping process, including any potential delays, fines, or penalties at customs. Additionally, any issues that arise during transportation—such as loss, theft, or damage—are the seller’s responsibility until the goods are delivered to the buyer.
4. Cash Flow Challenges
The costs associated with DDP shipping, such as duties, taxes, and customs clearance, must be paid upfront by the seller. This can create cash flow challenges, particularly for small businesses or those dealing with large shipments. Sellers must ensure they have the financial resources to cover these costs until they can recover them through the sale of goods.
5. Limited Control for the Buyer
While DDP shipping offers convenience, it can also limit the buyer’s control over the shipping process. The buyer may not have insight into the shipping timeline, the choice of carrier, or how the goods are handled during transit. This lack of transparency can be a disadvantage for buyers who prefer to be more involved in the logistics process.
When to Use DDP Shipping Agreement
DDP shipping is most beneficial in the following situations:
When the Buyer Lacks Experience: If the buyer lacks experience in handling customs clearance and import duties, DDP provides a hassle-free solution.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) Sales: DDP is often used for B2C transactions, where the buyer expects a seamless delivery experience without dealing with import procedures or additional charges.
High-Value Products: When shipping high-value products, DDP can help ensure that all logistics are carefully managed, reducing the risk of customs delays or unexpected charges.
Market Penetration: Sellers entering a new market may choose DDP to offer a better experience for new buyers by simplifying the delivery process and eliminating uncertainties around customs clearance and duties.
When to Avoid DDP Shipping Agreement
DDP shipping may not be the best choice in the following situations:
High Customs Duties: If the destination country has high import duties, the costs associated with DDP can significantly reduce the seller’s profit margin.
Unfamiliar Customs Regulations: If the seller is unfamiliar with the customs regulations of the destination country, the complexities of managing customs clearance may lead to delays, fines, or penalties.
Cash Flow Constraints: Sellers who face cash flow constraints may want to avoid DDP, as they must cover all duties, taxes, and shipping costs upfront, which can strain financial resources.
Buyer Preference for Control: In some cases, buyers may prefer to handle customs clearance themselves to ensure transparency, cost savings, or faster processing times.
DDP Shipping vs. Other Incoterms
DDP vs. FOB (Free on Board)
FOB: Under FOB, the seller is responsible for delivering goods to the port of origin and loading them onto the vessel. The buyer takes over responsibility once the goods are on board, including paying for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance.
DDP: In contrast, DDP places all responsibilities on the seller until the goods reach the buyer’s location, making it more convenient for the buyer but more costly for the seller.
DDP vs. CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight)
CIF: The seller covers the cost, insurance, and freight up to the destination port; however, the buyer is then responsible for customs clearance as well as local delivery. In this way, each party handles specific portions of the shipping process.
DDP: The seller manages the entire shipping process, including customs clearance and final delivery, providing a door-to-door service for the buyer.
The Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) shipping agreement offers a convenient and predictable solution for buyers by simplifying the logistics process and providing a door-to-door delivery experience. However, it comes with significant responsibilities and costs for the seller, including customs clearance, duties, and transportation risks. When deciding whether to use DDP, both buyers and sellers must weigh the advantages and disadvantages in light of their specific business needs, financial situation, and risk tolerance.
For businesses looking for a reliable freight forwarding partner that can manage DDP shipping effectively, Tonlexing offers comprehensive logistics solutions tailored to your needs. Our team has extensive experience in managing international shipments, ensuring smooth customs clearance, and providing seamless delivery to your customers. Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your international shipping needs.


