Air freight is an essential part of global trade, enabling businesses to transport goods quickly and efficiently across borders. Whether shipping urgent documents, high-value electronics, or perishable goods, air freight provides unmatched speed and reliability. However, navigating air cargo logistics requires understanding key players, shipping methods, costs, and best practices.
This guide covers everything you need to know about air freight, including service types, transit times, cost factors, and how to optimize your shipping process. By the end, you’ll have a complete understanding of air freight logistics and how to choose the best options for your business.

Table of Contents
Introduction to Air Freight
Air freight plays a critical role in global trade, providing businesses with a fast, reliable, and secure method of transporting goods across international borders. Unlike sea or rail freight, which can take weeks, air cargo shipments are completed in days, making it an ideal choice for time-sensitive and high-value goods.
Why Businesses Use Air Freight
- Speed and Efficiency: Air cargo offers the fastest delivery times, often within 1–7 days, depending on the destination and service level.
- Reliability: With strict flight schedules and minimal handling time, air freight ensures consistent and predictable transit times.
- Security: Airports and airlines follow strict safety measures, reducing the risk of theft and damage.
- Global Connectivity: Air freight networks cover nearly every country, allowing businesses to reach international markets quickly.
Industries That Rely on Air Freight
- Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, and semiconductor components require fast transportation to meet consumer demand.
- Pharmaceuticals & Medical Equipment: Vaccines, temperature-sensitive drugs, and medical devices need controlled environments and quick delivery.
- Automotive & Machinery: Urgent spare parts and high-value machinery components benefit from rapid transport.
- E-commerce & Fashion: Fast-growing online businesses rely on air cargo to ship high-demand products quickly to global customers.
- Perishable Goods: Fresh seafood, flowers, and dairy products depend on air freight to maintain product quality.
When to Choose Air Freight Over Other Shipping Methods
Air freight is ideal for:
- Urgent shipments that require quick delivery.
- High-value goods where security is a top priority.
- Small to medium-sized shipments that are cost-effective to transport via air.
- Perishable items that need refrigeration or special handling.
Although air freight has higher costs than sea or rail transport, the speed and reliability make it a preferred choice for businesses that prioritize fast delivery and minimal risk.

Key Players in the Air Freight Industry
The air freight industry is a highly coordinated network involving multiple stakeholders that ensure the smooth and efficient movement of cargo worldwide. Understanding the roles of these key players helps businesses optimize their shipping processes and avoid potential delays.
Airlines & Cargo Carriers
Airlines play a crucial role in air freight by offering dedicated cargo services or transporting goods in the belly of passenger aircraft. These companies manage cargo handling, flight operations, and logistics planning.
Major Air Cargo Airlines:
- FedEx Express: One of the world’s largest express transportation companies, specializing in time-sensitive deliveries.
- DHL Aviation: Offers international express services with a strong presence in Europe, the U.S., and Asia.
- UPS Airlines: A major cargo airline providing integrated supply chain solutions.
- Emirates SkyCargo: A leading global carrier offering wide-body aircraft for cargo shipments.
- Qatar Airways Cargo: One of the fastest-growing cargo carriers, known for its high-capacity freighter fleet.
- Lufthansa Cargo & Cargolux: European leaders in international freight operations.
Freight Forwarders
Freight forwarders serve as intermediaries between shippers and airlines, coordinating shipments from pickup to delivery. They provide value-added services such as cargo consolidation, customs clearance, and door-to-door logistics.
Top Freight Forwarders for Air Cargo:
- Tonlexing: Offers seamless air freight logistics, including customs handling and door-to-door solutions.
- Kuehne + Nagel: A global leader in freight forwarding with a strong air cargo division.
- DB Schenker: Provides integrated logistics solutions for businesses worldwide.
- Expeditors International: Specializes in time-critical shipments and supply chain optimization.
- DHL Global Forwarding: A division of DHL that manages complex freight forwarding operations.
Freight forwarders help businesses navigate the complexities of international shipping, ensuring efficient and cost-effective air cargo transport.
Customs Authorities & Regulatory Bodies
International and national regulatory bodies oversee air freight operations to ensure compliance with trade laws, aviation safety, and security regulations.
- International Air Transport Association (IATA): Establishes industry-wide standards for air cargo transportation and documentation.
- Customs & Border Protection (CBP): Regulates imports, ensures cargo security, and enforces duty compliance.
- Civil Aviation Authorities: National agencies that monitor air freight safety regulations, including hazardous materials handling.
- World Customs Organization (WCO): Sets global trade standards, including HS code classification for goods.
Understanding the roles of these key players in the air freight industry helps businesses streamline their logistics operations, minimize delays, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Types of Air Freight Services
Different air freight services are designed to meet varying business needs, balancing cost, speed, and cargo requirements. Selecting the right type of air freight service is essential for optimizing logistics and ensuring timely deliveries.
Standard Air Freight
- Transit Time: 3–7 days
- Best For: Businesses that require a balance between cost and speed.
- Common Cargo: Consumer goods, apparel, auto parts, electronics, and industrial components.
- Details: Standard air freight is widely used for regular shipments that do not require urgent delivery but still need faster transit than sea freight. It provides competitive pricing while ensuring reliable shipping times.
Express Air Freight
- Transit Time: 1–3 days
- Best For: Time-sensitive shipments that require immediate transportation.
- Common Cargo: Medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, urgent manufacturing parts, perishable food, and high-value goods.
- Details: Also known as priority air freight, this service ensures the fastest possible delivery by using premium flight schedules with direct routes. Express air freight is commonly offered by global courier companies such as FedEx, DHL, and UPS.
Consolidated Air Freight (Economy Air Freight)
- Transit Time: 5–10 days
- Best For: Businesses looking for cost-effective air freight solutions.
- Common Cargo: General consumer goods, industrial machinery, and non-urgent e-commerce shipments.
- Details: This service combines multiple shipments from different businesses into one consolidated load, optimizing space and reducing costs. While slightly slower than standard air freight, it offers significant savings for businesses shipping lower-priority goods.
Air Charter Services
- Transit Time: As required (on-demand service).
- Best For: Exclusive, oversized, emergency, or specialized cargo.
- Common Cargo: Large-scale event logistics, humanitarian aid, military shipments, oil and gas equipment, and critical medical supplies.
- Details: Air charter services allow businesses to rent an entire aircraft for their cargo, ensuring immediate and direct transportation. This is the most expensive air freight option but provides maximum flexibility and rapid delivery.
By choosing the right air freight service, businesses can optimize shipping costs while ensuring their cargo reaches its destination efficiently and on time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Air Freight
Air freight is widely used for its speed and reliability, but it also comes with limitations in terms of cost and capacity. Businesses should weigh these factors to determine if air freight is the best option for their logistics needs.
Advantages of Air Freight
✅ Fastest Transit Times
- Air freight offers the shortest shipping time compared to sea or rail transport, making it ideal for time-sensitive shipments.
- Transit times typically range from 1–7 days, depending on the service selected.
✅ Reliable Scheduling
- Flights operate on fixed schedules, reducing the risk of unexpected delays compared to ocean freight, which can be affected by port congestion or adverse weather conditions.
✅ Global Reach
- Air freight provides direct access to international airports worldwide, ensuring efficient connectivity between major business hubs.
- Ideal for landlocked destinations or remote areas where sea or rail transport is not viable.
✅ High Security & Minimal Cargo Damage
- Airports have strict security protocols, reducing the risk of theft or tampering.
- The limited handling process minimizes damage to fragile or high-value cargo.
✅ Lower Inventory Holding Costs
- Faster transit times allow businesses to maintain lower inventory levels and reduce warehousing costs.
- Useful for just-in-time (JIT) supply chain models in industries like electronics and pharmaceuticals.
Disadvantages of Air Freight
❌ Higher Costs
- Air freight is significantly more expensive than sea or rail transport.
- Costs are calculated based on weight and volume, making it impractical for heavy or bulky goods.
❌ Weight & Size Limitations
- Airlines impose strict size and weight restrictions on cargo.
- Large machinery, heavy equipment, or oversized goods may not be suitable for air transport.
❌ Environmental Impact
- Air transport has a higher carbon footprint compared to sea freight.
- Businesses focused on sustainability may need to consider carbon offset programs or alternative shipping methods.
By understanding these advantages and disadvantages, businesses can make informed decisions when selecting air freight for their logistics operations.
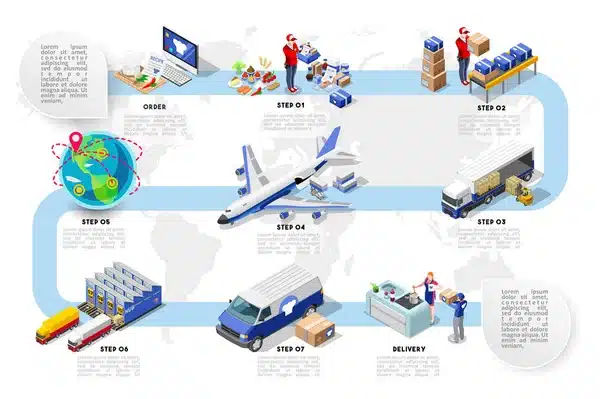
Air Freight Process: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Shipping via air freight involves multiple steps, from cargo booking to final delivery. Understanding this process helps businesses plan efficiently and avoid potential delays.
Cargo Booking & Pickup
- The shipper books air freight services with a freight forwarder or airline.
- Goods are packed according to airline regulations (e.g., IATA packaging guidelines).
- A trucking service picks up the cargo and transports it to the departure airport.
Customs & Security Checks
- Shipments undergo security screening to comply with aviation regulations.
- Customs authorities review shipping documents such as the commercial invoice, packing list, and air waybill (AWB).
- If required, goods may be physically inspected before being cleared for departure.
Air Transport & Handling
- Cargo is loaded onto the aircraft, either in the belly of a passenger plane or on a dedicated freighter.
- Some shipments may transit through hub airports (e.g., Dubai, Frankfurt) before reaching the final destination.
- Airlines ensure proper handling of sensitive or perishable cargo using temperature-controlled or secure storage solutions.
Customs Clearance at Destination
- Upon arrival, the consignee (buyer) or their customs broker submits necessary import documentation.
- Customs officers assess import duties, taxes, and regulatory compliance.
- If no issues arise, the cargo is released for final delivery.
Final Delivery
- The consignee arranges inland transportation (trucks, rail, or couriers) to their warehouse or distribution center.
- Real-time tracking allows importers to monitor delivery progress.
By following these steps, businesses can ensure a smooth and efficient air freight shipping process, minimizing delays and unexpected costs.
Key Documentation in Air Freight
Proper documentation is essential for air freight shipments to clear customs smoothly and comply with international regulations. Below are the critical documents required:
Airway Bill (AWB)
- A legal contract between the shipper and airline.
- Contains shipment details, including shipper and consignee information, flight details, and cargo description.
- Acts as a receipt for the airline and a tracking reference for the consignee.
Commercial Invoice
- Provides a detailed description of the shipped goods, including value, quantity, and HS code classification.
- Used by customs authorities to assess duties and taxes.
- Must match the details on the AWB and other shipping documents.
Packing List
- Specifies packaging details such as weight, dimensions, and the number of items per package.
- Helps with cargo handling, loading, and unloading at the airport.
- Important for customs inspections and verification of goods.
Certificate of Origin (CO)
- Confirms the country where the goods were manufactured.
- Required for preferential trade agreements that offer reduced tariffs.
- Must be issued by an authorized organization, such as a Chamber of Commerce.
Import Licenses & Permits
- Required for restricted or regulated goods such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, or electronics.
- Issued by government agencies or regulatory bodies depending on the type of cargo.
- Non-compliance may result in shipment delays or rejections by customs.
Additional Documentation (If Applicable)
- Dangerous Goods Declaration – Required for hazardous materials (e.g., lithium batteries, chemicals).
- Health & Safety Certificates – Necessary for perishable or medical shipments.
- Insurance Certificate – Provides coverage details for high-value shipments.
Ensuring that all documents are complete and accurate helps businesses avoid customs delays, penalties, or additional storage charges during air freight shipping.
Air Freight Rates and Cost Factors
Air freight pricing is influenced by multiple variables, including weight, distance, fuel prices, and market demand. Understanding these factors helps businesses plan and optimize shipping costs.
Chargeable Weight Calculation
Air freight costs are determined based on the higher of the following two values:
Actual weight (kg): The total physical weight of the shipment.
Volumetric weight (kg): Used for lightweight but bulky shipments. Calculated using the formula:
Volumetric Weight (kg) = (Length × Width × Height in cm) ÷ 6000
Example: If a shipment measures 100 cm × 80 cm × 60 cm and weighs 60 kg, the volumetric weight is:
(100 × 80 × 60) ÷ 6000 = 80 kg
Since the volumetric weight (80 kg) is higher than the actual weight (60 kg), the air freight cost is based on 80 kg.
Factors Affecting Air Freight Costs
- Shipping Distance & Route: Longer routes and indirect flights cost more due to multiple handling points.
- Fuel Prices: Fluctuations in jet fuel costs impact air cargo surcharges.
- Customs Duties & Taxes: Additional fees imposed by destination countries may increase total costs.
- Seasonal Demand: Rates increase during peak shipping seasons such as holiday periods, Chinese New Year, and Black Friday.
- Handling & Security Fees: Additional costs may apply for specialized handling, perishable goods, or high-value items requiring extra security.
By planning ahead and selecting the right air freight service, shippers can optimize costs and improve efficiency.

Tips for Successful Air Freight Shipping
To ensure a smooth and cost-effective air freight experience, businesses should follow these key best practices:
Choose the Right Air Freight Service
- Express Air Freight – Best for urgent shipments that require fast delivery.
- Standard Air Freight – Suitable for general cargo with flexible delivery times.
- Consolidated Air Freight – Cost-effective for smaller shipments combined with other cargo.
Plan Ahead to Avoid Peak Season Surcharges
- Book shipments in advance to secure lower rates, especially during high-demand seasons like Chinese New Year, Black Friday, and major shopping events.
- Monitor fuel surcharges and market fluctuations to choose the best shipping time.
Ensure Accurate Documentation
- Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, and Airway Bills (AWB) correctly to prevent customs clearance delays.
- Check import regulations in the destination country, especially for restricted items like electronics, lithium batteries, and perishables.
Partner with a Reliable Freight Forwarder
- Work with experienced logistics providers like Tonlexing to manage shipping, customs clearance, and final delivery.
- Use a freight forwarder with global network coverage to optimize routes, transit times, and pricing.
By following these strategies, shippers can minimize costs, reduce delays, and ensure a seamless air freight process.
Why Choose Tonlexing for Air Freight?
When shipping goods internationally, choosing the right logistics partner is crucial for a smooth and cost-effective experience. Tonlexing offers comprehensive air freight solutions tailored to your business needs.
Comprehensive Freight Services
- Air, sea, and rail freight solutions for seamless global shipping.
- Flexible options including express, standard, and consolidated air freight.
Expert Customs Handling
- Hassle-free customs clearance in major markets such as the USA, Europe, Middle East, and Africa.
- Assistance with import/export regulations, documentation, and duty calculations.
Transparent Pricing & Cost Savings
- No hidden fees – clear cost breakdowns, including freight rates, customs duties, and additional charges.
- Competitive rates with customized solutions to optimize costs.
Reliable Tracking & 24/7 Support
- Real-time shipment monitoring to keep you updated on cargo status.
- Dedicated customer support available 24/7 to handle queries and logistics coordination.
📦 Contact Tonlexing today for expert air freight solutions and a seamless shipping experience!


